The previous article takes part of the introduction of HCX Cloud and HCX Connector.
Also about what is needed to use HCX in the source site and the destination site.
Now we are going to talk about Site Pairing, Service Mesh and Migration Types
Site Pairing
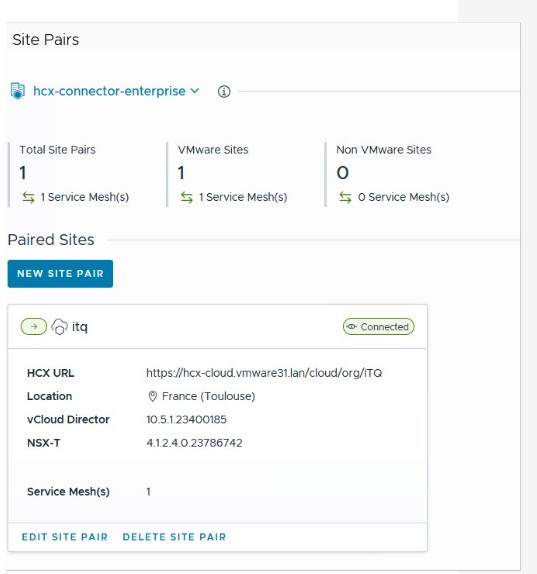
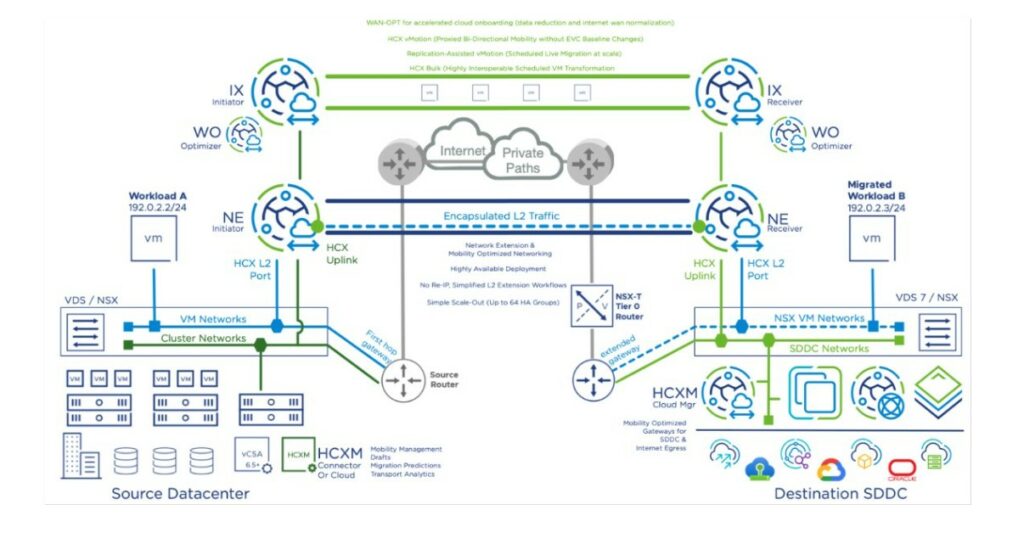
A vSphere-based site is a vSphere installation where HCX Connector or HCX Cloud has been deployed and activated. For these sites, HCX supports a full range of management and mobility services when paired with other vSphere-based sites.
VMware vSphere-based sites can be either private (on-premises) or public clouds. HCX Connector sites serve as the source of mobility and network extension operations. HCX Cloud sites serve as the target of HCX operations, or as the source and target site in cloud-to-cloud configurations.
Service Mesh
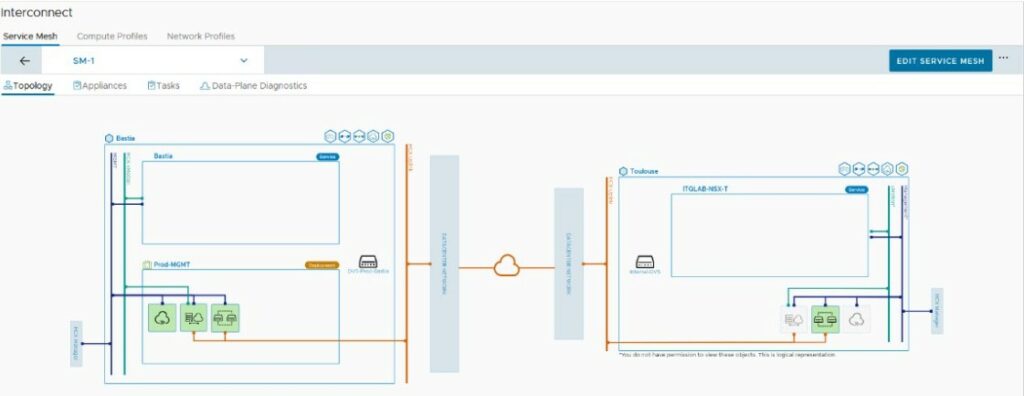
The Service Mesh is used to create a secure optimized transport fabric between two paired sites.
The procedures for creating a Service Mesh vary based on whether the site pairing is between two vSphere-based HCX installation, or between a vSphere-based HCX site and a non-vSphere HCX site
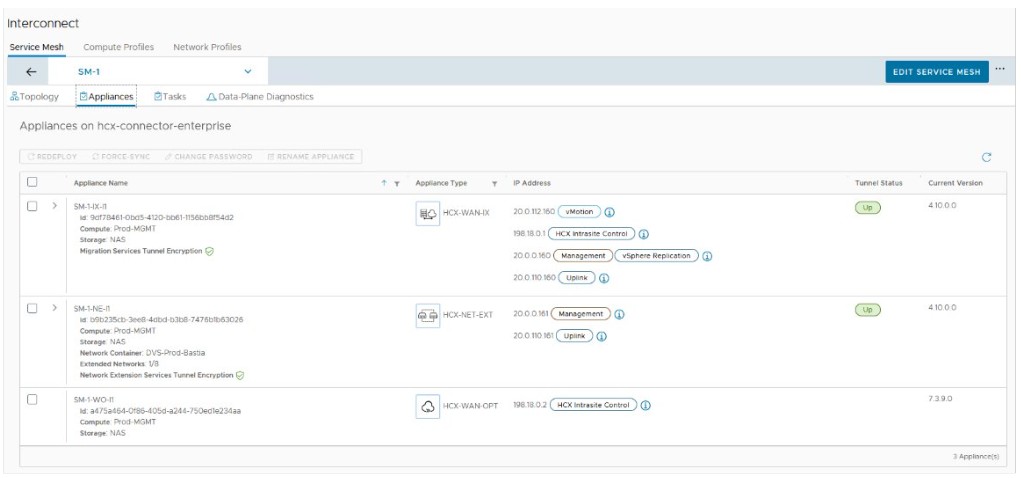
When HCX Migration, Network Extension, WAN Optimization, and Disaster Recovery services are activated, HCX deploys the associated virtual appliances in the source site and corresponding « peer » virtual appliances on the destination site. The Service Mesh activates the configuration, deployment, and serviceability of these Interconnect virtual appliance pairs
Service Mesh Benefits
- Uniformity: the same configuration patterns at the source and remote sites.
- Reusability: Once a compute profile is created, it can be used to connect to multiple HCX sites.
- Multi-site ready: Compute Profiles and Network Profiles can be shared across multiple sites.
- Ease of reconfiguration: New capability to pool datastores or modify them after deploying an Interconnect network structure.
- Scale-out deployment: The HCX-IX appliance can be deployed per cluster or a single HCX-IX can be shared across multiple clusters.
- Parallel execution ensures faster Interconnect deployments (in under 5 minutes).
- Lockless model ensures parallel configuration of network stretches
- Interfaces display a clear deployment diagram.
- Task-tracking features provide incremental details for each step of the progress of operations.
- Preview of required firewall rules to avoid configuration difficulties.
Service Mesh topology
Service Mesh Appliances
Migration Types
Bulk Migration
- This migration method uses the VMware vSphere Replication protocols to move the virtual machines to a destination site.
- The Bulk migration option is designed for moving virtual machines in parallel.
- This migration type can set to complete on a pre-defined schedule.
- The virtual machine runs at the source site until the failover begins. The service interruption with the bulk migration is equivalent to a reboot.
vMotion Migration
- This migration method uses the VMware vMotion protocol to move a virtual machine to a remote site.
- The vMotion migration option is designed for moving single virtual machine at a time.
- The virtual machine state is migrated. There is no service interruption during an HCX vMotion migration.
Cold Migration
- This migration method uses the VMware NFC protocol. It is automatically selected when the source virtual machine is powered off.
We close this part with the migration types. In the next part we will see the HCX Migration workflow